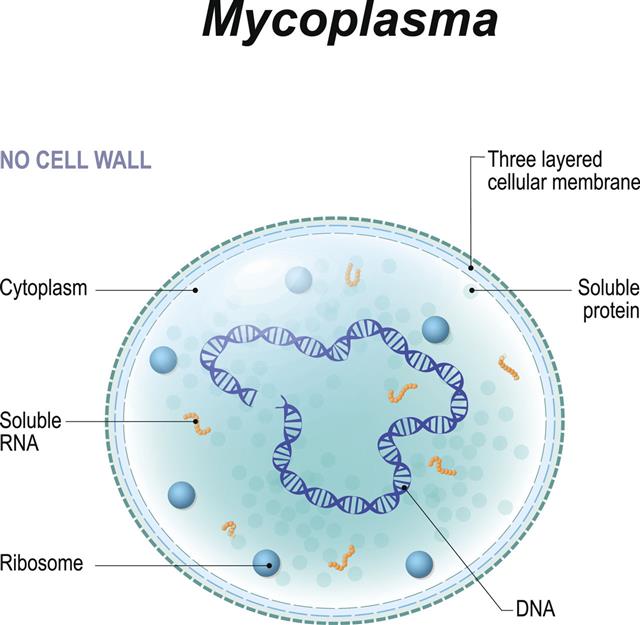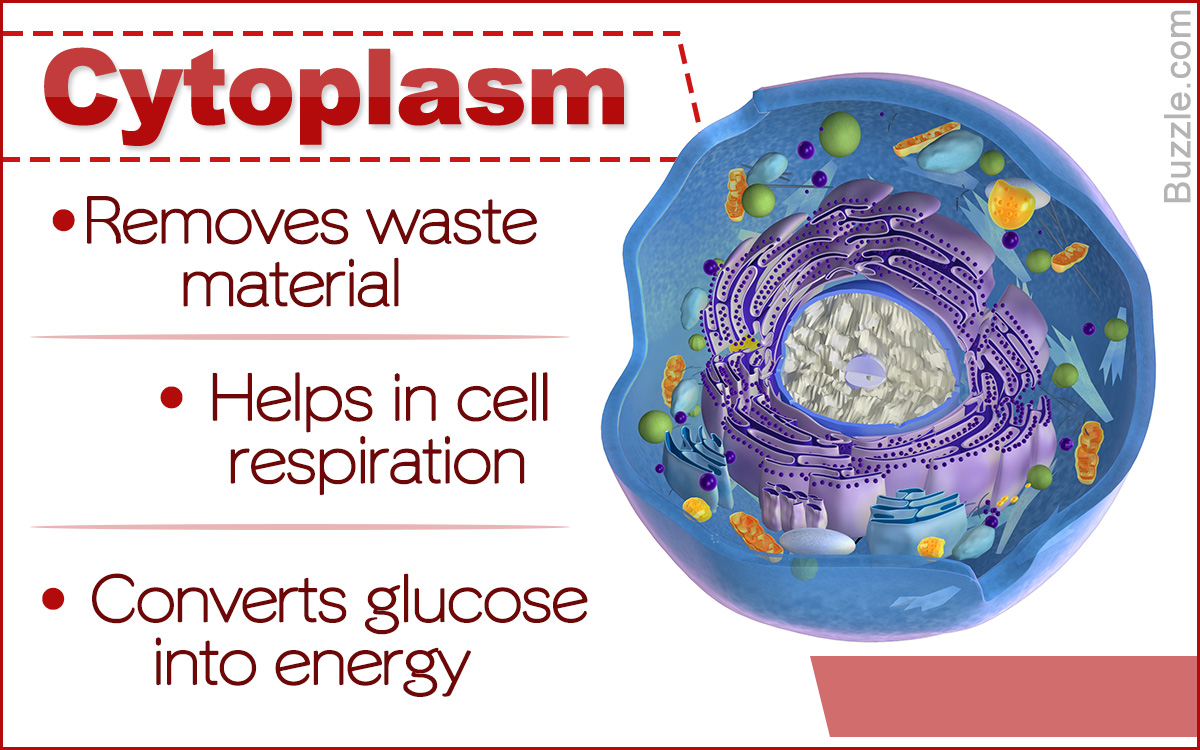
Cells are the building blocks of life and each cell houses some organelles that are suspended in a gel-like substance called cytoplasm, which plays a vital role in cellular functions.
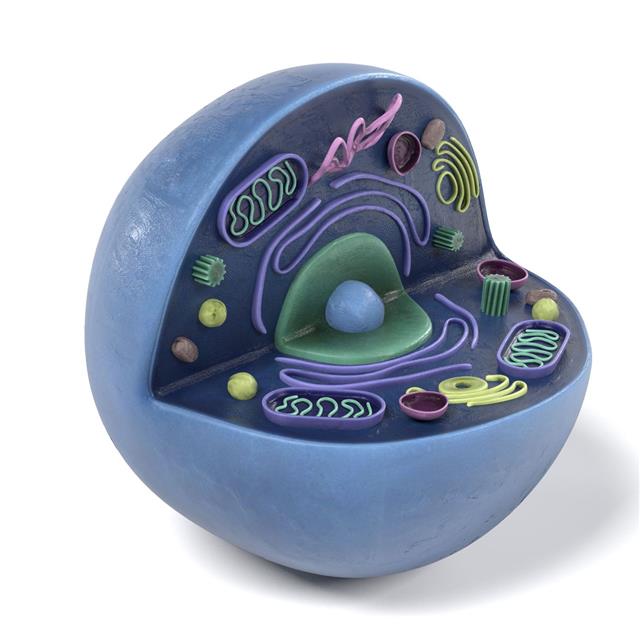
It is a common fact that cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. Each type of cell has its own functions, which are carried out by its organelles. It is the joint effort of these structures that make a cell work efficiently. The components of a cell are enclosed within the cell membrane. Though this membrane is like a barrier between individual cells, it allows selective entry of molecules and ions inside the cell. These molecules and ions cross the cell membrane and travel through the cytoplasm to reach the organelles. The internal organelles of the cell are suspended in the cytoplasm, which is a gelatinous fluid that fills the interior of the cell.
What is Cytoplasm?
Basically, there are two types of cells – eukaryotic and prokaryotic. The main difference between the two is that the latter ones lack nucleus and some other organelles. The basic structure of an eukaryotic cell includes a cell nucleus with DNA, ribosomes, vesicles, endoplasmic reticulum (both rough and smooth), Golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, vacuole, centrioles, lysosome, cytoplasm and plasma membrane. In prokaryotic cells, all internal organelles including the genetic material, are suspended in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotic cells, the contents of the nucleus do not have any contact with the cytoplasm.
As mentioned above, cytoplasm fills the inner space of the cell. In case of eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm fills the area between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Cytoplasm is classified into two types – ectoplasm and endoplasm. Ectoplasm represents the outer non-granular part of the cytoplasm, whereas endoplasm is the granular cytoplasm found in the inner regions of a cell.
Cytoplasm contains cytosol, the organelles of the cell (except the nucleus) and some insoluble substances. Cytosol is the liquid part of the cytoplasm, excluding the internal organelles. Cytoskeleton (a network of microfilaments) is suspended in the cytosol. The internal organelles include the mitochondria, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, etc. Certain insoluble substances are also found in the cytoplasm. They are called cytoplasmic inclusions. The common ones are glycogen, starch and lipids. Various enzymes, fatty acids, sugars, amino acids and salts are also found dissolved in the cytoplasm.
Functions of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm provides support to the internal structures of the cell. It houses a network of protein filaments called cytoskeleton, which helps to maintain the shape and consistency of the cell. These filaments hold the internal organelles in place, which would otherwise form a group, near the bottom of the cell.
Another important function of cytoplasm is its role in the movement of the internal organelles as well as the cell in whole. While the actin filaments in the ectoplasm facilitate movement of the cell in whole, the inner protein filaments help the organelles and other structures to move inside the cell.
Apart from storing various nutrients, the cytoplasm is that location where numerous vital cellular reactions (like anaerobic glycolysis and protein synthesis) and activities take place. This gel-like substance helps the cell to carry, absorb and process the necessary nutrients.
The enzymes in the cytosol break down large molecules, thereby helping the organelles to use them. For example, the mitochondria in the cell cannot use the glucose molecules present in the cytoplasm. The enzymes in the cytosol break down these glucose molecules into pyruvate molecules, which are then used by the mitochondria. Exchange of chemicals between the organelles is also one among the different cytoplasm functions.
In short, cytoplasm is the binding factor for the organelles inside the cell and it synchronizes the various cellular functions. The above said is only a brief overview about the functions of cytoplasm in a cell. You may conduct a detailed study to know more about the subject.