Are you interested in the wonderful world of microscopic organisms? The following article explains some facts about a group of microorganisms called diatoms.
Diatoms constitute a major part of algae, and most of them are unicellular organisms. They occur in various forms: filamentous, fan-shaped, zigzag, and ribbon-shaped colonies, and they can be noticed easily in the freshwater and marine environment. Major examples are, fragillaria, meridion, tabellaria, etc.
Facts
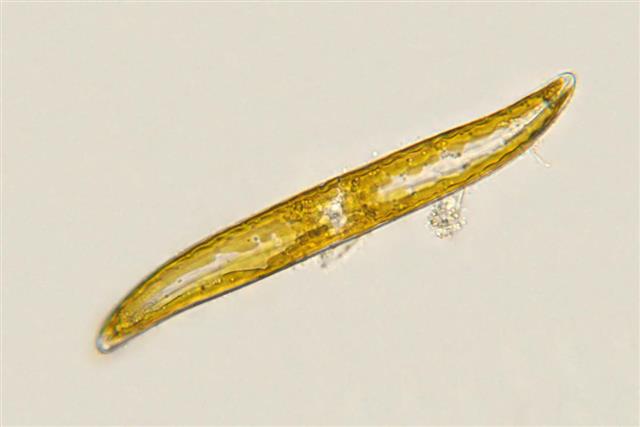
Diatoms are microscopic, single-celled, or colonial plant-like organisms, whose cell walls are composed of silicon dioxide (silica). There are numerous holes or areolae on their shells (or tests), which are visible under a microscope.
They are found on damp surfaces, in the oceans, rivers, lakes, streams, estuaries, puddles, on wet rocks, and in various soils. Most diatoms are microscopic, but some species are as long as 2 millimeters. They usually do not move, but few species use the flagella for locomotion.
Regarding their classification, diatoms belong to the class Bacillariophyceae, and there are more than 200 genera of this organism. They are classified as either protists or chromists. According to some estimates, there are approximately 100,000 existing species of this organism. Two types of diatoms are present: the round centrales, and the long or pen-shaped pennales.
They grow a silica shell that is preserved in underwater sediments after their death. This test is known as frustule, which is different for each species, so you can identify them by observing through a microscope. These frustules exhibit two asymmetrical sides with a split between them; hence the name diatoms. They are mostly yellowish or brownish, and they have chlorophyll A, chlorophyll C, and carotenoid fucoxanthin that occurs in plastids. They produce food by photosynthesis, and are great suppliers of oxygen.
Diatoms undergo asexual reproduction as they reproduce by cell division. They becomes smaller with each round of replication. Very small species may follow a sexual mode of reproduction, which allows the growth of a relatively large zygote.
As they die, diatoms tests accumulate in the ooze, and form the material known as diatomaceous earth, which is also known as kieselguhr. It found in the form of a soft, chalky, and light-weight rock that is called diatomite, which is used as an insulating material to absorb both heat and sound. It is used to manufacture dynamite, other explosives, filters, abrasives, etc. It is sometimes used in gardening as a pest control.
Diatoms play an important role in the formation of the Earth’s structure, as the limestone layers are deposited by them, and occurrence of petroleum has partly been possible due to these organisms. Their communities provide a tool for monitoring past and present environmental conditions. They are useful in studies of water quality. Different species of this organism prefer different temperatures. Therefore, scientists can estimate the temperature of the water where they live. Diatoms are mostly present in great numbers, and their size helps to indicate lateral water movement, and how well the water is mixed.